The [Read data] element (Fig. 1) obtains field values of the needed records from the database for later use down the process flow.
Fig. 1 The [Read data] process element

Whenever a business process needs to work with the data from Creatio database, the corresponding field values must be fetched (i.e., “read”). The fetched data is stored in the outgoing parameters of the [Read data] element.
The [Read data] element can read data from any object, regardless of the access permissions of the user who runs the process.
The element has four modes (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 Selecting a mode for a [Read data] element
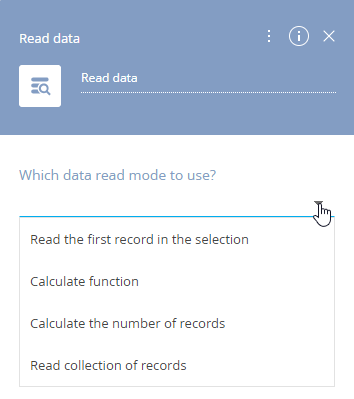
Read the first record in the selection
The [Read data] element obtains a list of records that match a filter, sorts it and reads field values of the first record in the filtered and sorted list. For example, you can get the subject, type and assignee of a specific activity.
Calculate function
The [Read data] element obtains a list of records that match a filter, and then calculates the specified function (sum, average, minimum or maximum) by the values of a specific column for filtered records. For example, you can calculate the duration of all activities of a specific user for a period. The following functions can be calculated:
-
Sum (numeric columns only) – the element calculates the sum in the specific columns of the records that match the filter.
-
Average (numeric columns only) – the element calculates the arithmetic mean of the values in the specified column for the records that match the filter.
-
Minimum (date and numeric columns) – the element analyzes the records that match the filter and determines the minimum value in the specified column.
-
Maximum (date and numeric columns) – the element analyzes the records that match the filter and determines the maximum value in the specified column.
The function result is passed into the element’s outgoing parameter.
Calculate the number of records
The [Read data] element obtains a list of records that match a filter, then calculates the number of records in the list and passes the result in its outgoing parameter. For example, you can calculate the number of accounts assigned to a specific account manager. Additionally, this function is useful for determining whether specific records exist at all, for example, whether a contact with certain name or phone number exists in the database.
Read collection of records
The [Read data] element obtains a list of records that match a filter, sorts it and reads field values of a set number of records (e.g., first 50 records in the filtered and sorted list).
The data obtained from multiple records is passed to a special parameter of the “Collection” type. Collection parameters contain nested parameters (Fig. 3), which represent columns in the collection of records. For example, if you read names and job titles of all contacts from a specific account, the resulting collection parameter will contain the nested parameters – “Full name” and “Job title”.
Fig. 3 An example of a collection parameter
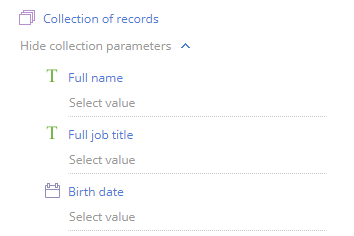
An actual collection of read records would look like this:
| Full name | Job title | Birth date |
|---|---|---|
| Jane Barber | Account manager | 04/12/1991 |
| Aaron Shepard | Sales manager | 10/24/1985 |
| Kate Smith | System administrator | 12/05/1989 |
Read more about using data collections in the “Working with collections” article.
Use cases
Information on how to use each of the modes is available below:
-
How to read data from a record that matches certain criteria
-
How to calculate sum, minimum, maximum and average of several records
-
How to calculate the number of records that match a condition
Next
•[Modify data] process element
•[Delete data] process element
•[Change access rights] process element
•[Script task] process element






