Configure a prediction business process
Once your prediction model is created, set up the actual predicting as a business process using the [Predict data] process element. This gives you complete control as to what records are predicted and when.
Example of configuring a business process with a lookup field prediction
You can set up a prediction of the account category whenever a new account with an empty [Category] field is saved (Fig. 1).
In this example, we will be using the account category prediction model created earlier.
Fig. 1 An example of ML model implementation process
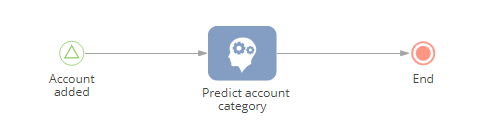
To implement this:
1.Create a new business process fro the process library and add the [Signal] start event on its diagram. The start event should be triggered whenever a new record in the [Accounts] section is added. Signal element parameters (Fig. 2):
Fig. 2 Signal element parameters
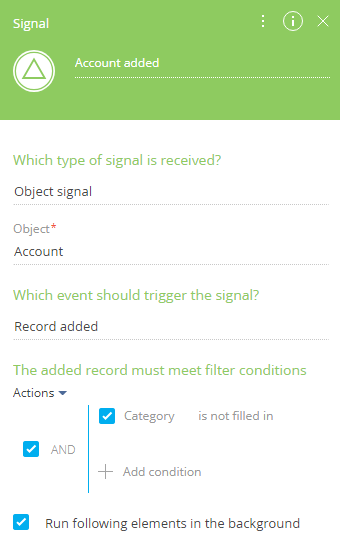
a.[Which type of signal is received?] - “Object signal.”
b.[Object] - “Account.”
c.[Which event should trigger the signal?] - “Record added.”
d.[The added record must meet filter conditions] – “Category is not filled in.”
e.[Run following elements in the background] – “true.” This way, all preceding system operations of the process will be performed in the background without displaying the loading mask.
2.Add the [Predict data] element on the diagram. Set up the element parameters (Fig. 3):
Fig. 3 [Predict data] element setup area
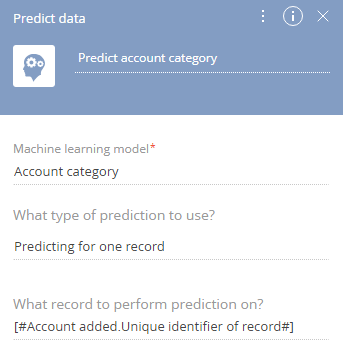
a.In the [Machine learning model] field, choose the prediction model to use. For example, to predict the category of the account, select the “Account category” model created earlier. The model setup is described in the “Lookup value prediction” article.
Note
Prediction models have to be trained before they can be used in the business process. If the model is not trained, it will not be available for selection in the [Predict data] element.
b.[What type of prediction to use?] - “Predicting for one record”.
c.In the [What record to perform prediction on?] field, click the  button and select [Process parameter]. In the window that appears, go to the [Process elements] tab and select the signal created in the previous step, and then select [Unique identifier of record].
button and select [Process parameter]. In the window that appears, go to the [Process elements] tab and select the signal created in the previous step, and then select [Unique identifier of record].
3.Save the process.
As a result, whenever the [Predict data] element is triggered during a business process, it will use the specified ML model to predict the data of the specified record. In our case, the [Category] field value will be predicted and populated each time a new record is saved in the [Accounts] section. The prediction will be based on the values specified by users when populating the [Category] field of historical records.
Example of a business process with recommendation prediction
You can set up running product recommendation predictions for accertain type of product to hold an advertising campaign (Fig. 4). For example, you can manually run a business process to recommend five products of a “Motherboards” type to all contacts of a “Customer” type.
In this example, we will be using the product recommendation model created earlier.
Fig. 4 Example of a business process with recommendation prediction
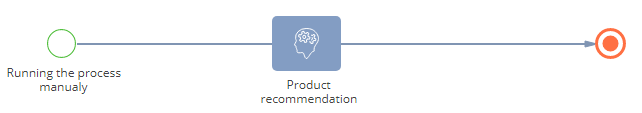
To implement this:
1.Create a new business process from the process library. Use the [Simple] start event to start the business process manually. The event is added to the diagram by default.
2.Add the [Predict data] element on the diagram. Set up the element parameters (Fig. 5):
Fig. 5 Setting up parameters of the [Predict data] element
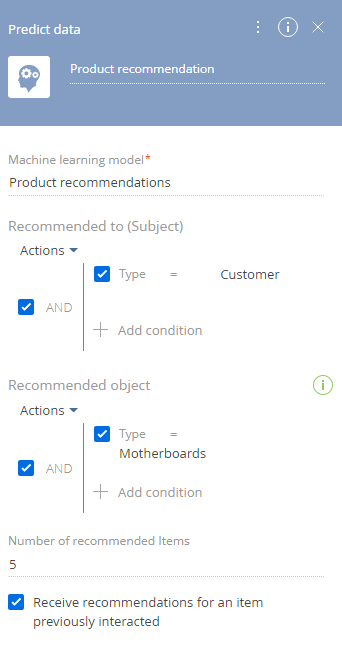
a.[Machine learning model] – specify the name of the recommendation model.
b.[Recommended to (Subject)] – specify the filter. Select all or specific contacts that will receive recommendations. The filter must be specified to validate the element. For our example, select the contacts of the “Customer” type.
c.Recommended object – specify the filter if you need to restrict the recommendation selection to solve a specific business task. For example, you can only recommend products of a certain type to your customers. In our example, these are motherboards.
d.[Number of recommended items] – specify how many records the recommendation list should contain. For example, you can restrict the number of recommendations to five.
e.[Receive recommendations for an item previously interacted] – select the checkbox to include only the products that involved interaction into the recommendations.
3.Add the terminate event and save the process.
As a result, whenever the [Predict data] element is triggered during a business process, it will use the specified ML model to generate a list of recommendations. In our example, the selection of training records will be restricted by the “Motherboards” product type. The list of recommendations consisting of five records will be generated for all contacts of the “Customer” type.
See also
•Basic predictive analysis glossary
•Numeric field value prediction






