Deploying the synchronization service via Kubernetes
To deploy the Exchange Listener synchronization service in Docker:
1.Set up the target environment first:
a.The Kubernetes cluster. Read more about how to set up and manage the cluster on the Kubernetes documentation website.
b.The “Helm” package manager. Read more about installing the package manager on the Helm documentation website.
2.Install Redis. Use the GitHub website to learn more about how to install Redis using Helm.
Example of a command for installing Redis:
helm install --namespace default --set usePassword=false --set=slave.persistence.enabled=false --set master.persistence.enabled=false --set cluster.enabled=false redis bitnami/redis
In this example:
•default – the name of the namespace where Redis will be installed;
•redis – an arbitrary name for the Redis instance.
3.Install the Exchange Listener module. To install the module, download the helm package. Find the available parameters of the helm package in the ”Available parameters of the Exchange Listener helm package” table.
Attention
For newer Kubernetes versions, specify the API version and add the following parameter:
--set apiVersion=apps/v1
Example of a command for installing Exchange Listener using the service address and relative path:
helm install --set env.host=<redis_host> --set ApiUrl=<kubernetes_url> --set ingress.path=<listener_path> --set apiVersion=apps/v1 --namespace <namespace name> exchangelistener </path/to/helm/exchangelistener.tgz>
In this example:
•<redis_host> – Redis server address;
•<Kubernetes_url> – Kubernetes URL or IP address.
Exchange Listener address: <kubernetes_url>/<listener_path>.
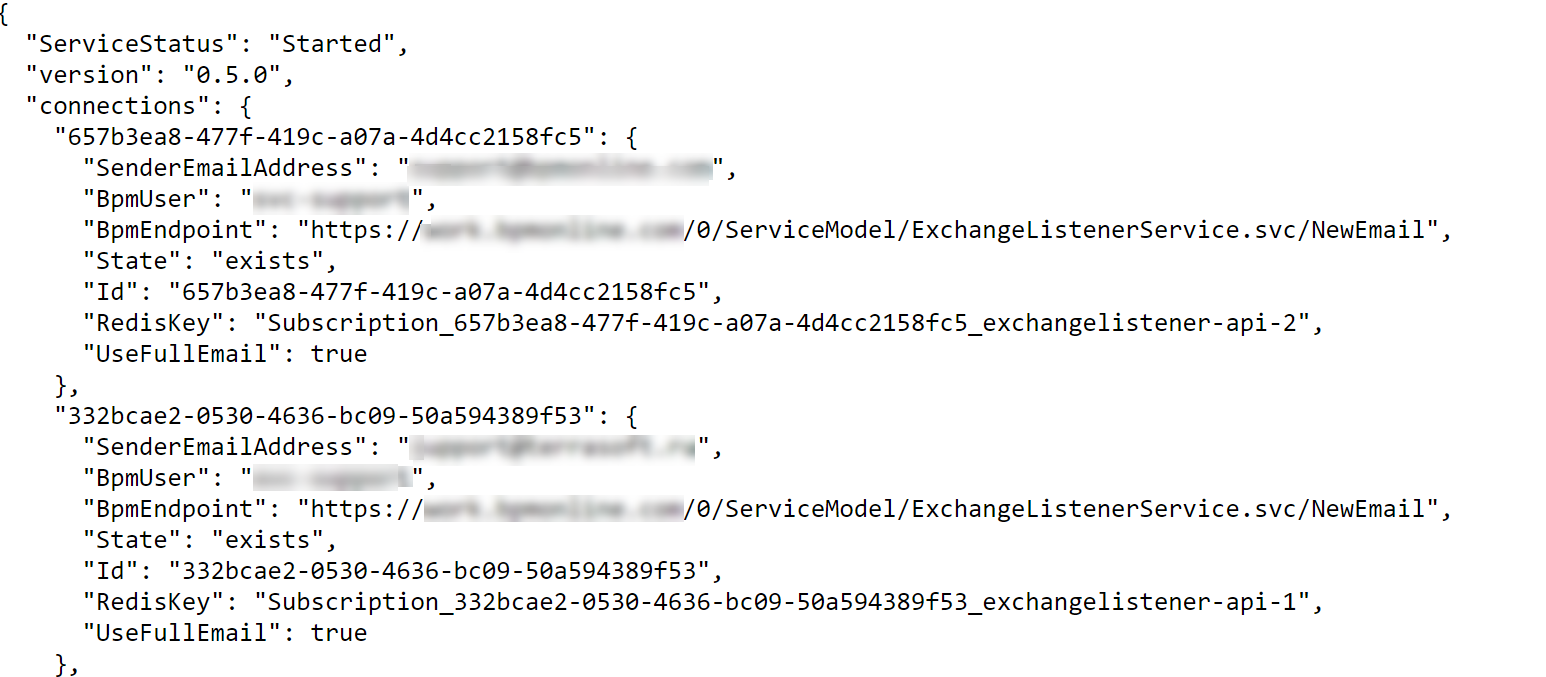
To check whether the Exchange Listener service is available, execute the following request: <kubernetes_url>/<listener_path>/api/listeners/status (Fig. 1).
Example of installing the Exchange Listener using Node IP and port address:
helm install --set env.host=<redis_host> --set service.type=<node_IP> --set service.nodePort=<node_port> --set apiVersion=apps/v1 --namespace <namespace name> exchangelistener </path/to/helm/exchangelistener.tgz>
Exchange Listener address – <node_IP:node_port>.
To check whether the address is available, execute the following request: <node_IP:node_port>/api/listeners/status (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Example of the Exchange Listener service response
Available parameters of the Exchange Listener helm package
|
Parameter |
Parameter description |
Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
replicaCount |
Number of StatefulSet processors |
2 |
|
service.type |
Service type. You can find more information about the Kubernetes service types in the Kubernetes documentation. |
ClusterIP |
|
service.nodePort |
If the service.type parameter equals NodePort, specify the external service port in this parameter. Read more about the NodePort type in the Kubernetes documentation. |
|
|
env.host |
Host address for Redis. |
|
|
env.port |
Host port for Redis. |
6379 |
|
env.base |
Database number for Redis. |
0 |
|
ingress.enabled |
Use address overriding via ingress. |
true |
|
ApiUrl |
Service address if ingress.enabled=true |
|
|
ingress.path |
Service relative path. |
|
|
log4Net.level |
Logging level by default. |
Info |
System requirements to servers
By default, separate nodes of the StatefulSet type process the requests based on 1 processor replica per 40 active mailboxes. The number of replicas depends on the replicaCount parameter. If the number of mailboxes increases, you need to increase the number of processors by specifying the needed value.
One processor requires 30% of the 2 GHz processor time and 850 Mb of RAM (disk storage is not used).
You can configure automatic scaling depending on the number of active subscriptions. To learn more, contact support@creatio.com.
See also






