Recommendation ML models create lists of objects (recommendations) that are likely to be linked to the “subject” records (the recommendation recipients). For example, you can recommend products to your customers based on what the similar clients purchase. Product recommendations with this prediction model are available in Creatio Sales lineup out-of-the-box. This article demonstrates how you can configure this prediction model without coding.
This product recommendation model training method is known as collaborative filtering. The collaborative filtering model uses the subject’s known preferences, as well as the preferences of the subjects that are similar to the target subject in certain criteria.
Creatio uses an item-based algorithm to predict the preferences. Creatio builds recommendation lists by summarizing and ranking the data about the interactions with the recommendation objects.
To implement a recommendation model:
-
Set up and train a new recommendation model.
-
Set up a business process with the Data prediction element.
1. Add a new recommendation prediction model
To create a prediction recommendation result:
- Open the ML models section in the Studio workplace.
- Click New – Recommendations.
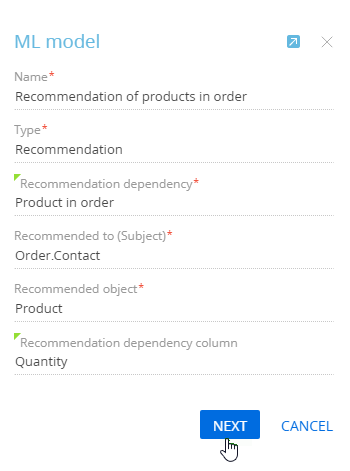
- Fill out the ML model creation mini page (Fig. 1):
- Name – the name of the prediction model. The name helps to identify the model in the ML models section list and select it when configuring the Data prediction business process element.
- Type – the ML model type. In our example, it is “Recommendation”. Creatio populates the field is populated automatically when you select the model in the previous step.
- Recommendation dependency – select the object that maintains a connection between the recommendation subject (for example, the customer) and the recommendation object (for example, the product). For instance, the customer is connected to the product through the “Product in order” object. When you select the connecting object, the mini page will display additional fields.
Fig. 1 The product recommendation model mini page
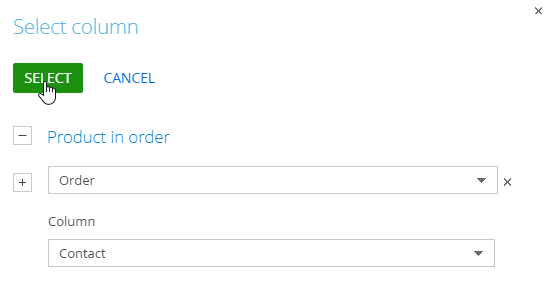
- Recommended to (Subject) – Creatio will generate the list of recommended objects for this column. In our example, Creatio will recommend the products to the contacts specified in the order. Click “+” and select the Order object, then the connected Contact object (Fig. 2):
Fig. 2 Selecting the recommendation subject column
-
Recommended object – select the recommendation object. In our example, it is the Product column of the “Product in order” object (Fig. 3):
Fig. 3 Selecting the recommendation object column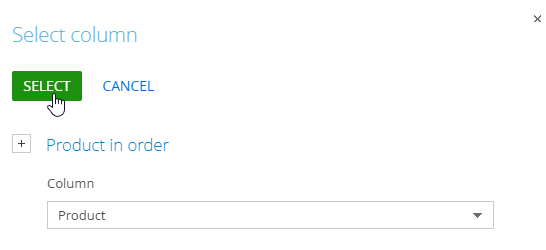
-
Recommendation dependency column – select a numeric column in the section, detail or lookup specified in the Recommendation dependency field. Creatio will use this column to grade the “quality” of dependency between the recommendation subject and the recommended object. For example, if you select the Quantity column, the number of products the contact ordered will determine the quality of dependency between the corresponding contact and different products. The more products a contact buys, the “higher” the contact’s dependency with the recommended object is, making Creatio more likely to recommend this product.
This field is not required. If you do not fill out the field, Creatio will evaluate the connection between the subject and the object in a binary way: “0” – connection does not exist; “1” – connection exists.
-
Click Next to save the mini page and open the product recommendation model setup page.
2. Set up the model parameters
After you fill out the required model fields, specify the parameters:
-
Which records should be included in the training dataset? – set up a filter Creatio will use to select the training records. For example, narrow down the training data range to products from the completed orders only. To do this, configure the following connected object filter: “Order.State = Closed”.
You do not need to specify the filter conditions. Creatio will use all available records for training by default.
-
Automatic model training settings – toggle the switch and set the parameters for automatic model retraining with the updated historical data.
-
Specify the interval between model training sessions in the Retrain after, days field. After the specified number of days, Creatio will retrain the model based on historical records that match the filter. The first model training starts when you click the Train model button. If you would rather not retrain the model, leave the field blank or enter “0.”
-
Specify the lowest prediction model accuracy threshold in the Quality metric lower limit field. When you train the model for the first time, this threshold will determine the minimum acceptable quality that the model needs to reach before Creatio can use it. If the model quality drops below this limit, the model is deemed unusable. We recommend setting the quality metric lower limit to at least 0.50. The machine learning model accuracy score ranges from 0.00 to 1.00 (higher is better). Creatio calculates the machine learning model accuracy by dividing the number of successful predictions by the total number of predictions. Use the Google documentation to learn more about how the prediction accuracy score is calculated.
-
-
Setting up saving prediction results – specify where Creatio will store the prediction results. You can save the prediction to any Creatio object that has the following required fields: Recommended to (Subject), Recommended object (“Lookup” type), and Probability (“Decimal” type) For example, you can add a Product recommendations detail to a contact page. Learn more: Create new detail.
If you select this detail as a prediction object, Creatio will select the columns of a suitable type automatically. If there is more than one such column, Creatio will automatically select the first column. You will be able to select a different column from the dropdown. If the object has no such columns, Creatio will not populate the field. We recommend checking the selected values before saving the model.
-
Specify the object that will store the recommendations in the Object field. It is usually a detail. Note that you can only specify an existing Creatio object. In this example, you can specify the preset Product recommendations detail. When you select an object, the Recommended to (Subject) and Recommended object fields become required.
-
Recommended to (Subject) — determines the recommendation subject. Creatio automatically populates the field with the value of the object column specified in the previous step. For example, “Contact.” If necessary, you can change the value by selecting another column of the appropriate type from the dropdown. The field is required.
-
Recommended object — determines the recommendation object. Creatio automatically populates the field with the value of the object column specified in the previous step. For example, “Product.” If necessary, you can change the value by selecting another column of the appropriate type from the dropdown. The field is required.
-
Probability — ranks the records. In this example, the higher the column value is, the more likely the opportunity is to succeed. Creatio automatically populates the field with the value of the object column specified in the previous step. For example, “Probability.” If necessary, you can change the value by selecting another column of the appropriate type from the dropdown. The field is required.
-
ML model — specifies the name of the ML model used for the prediction. In this example, specify the recommendation model name. Creatio automatically populates the field with the value of the object column specified in the previous step. For example, “ML model.” If necessary, you can change the value by selecting another column of the appropriate type from the dropdown. We recommend filling out this field if you use several prediction models.
-
Prediction date — specifies when the prediction was made. Creatio automatically populates the field with the value of the object column specified in the previous step. For example, “Prediction date.” If necessary, you can change the value by selecting another column of the appropriate type from the dropdown. (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4 The product recommendation model parameters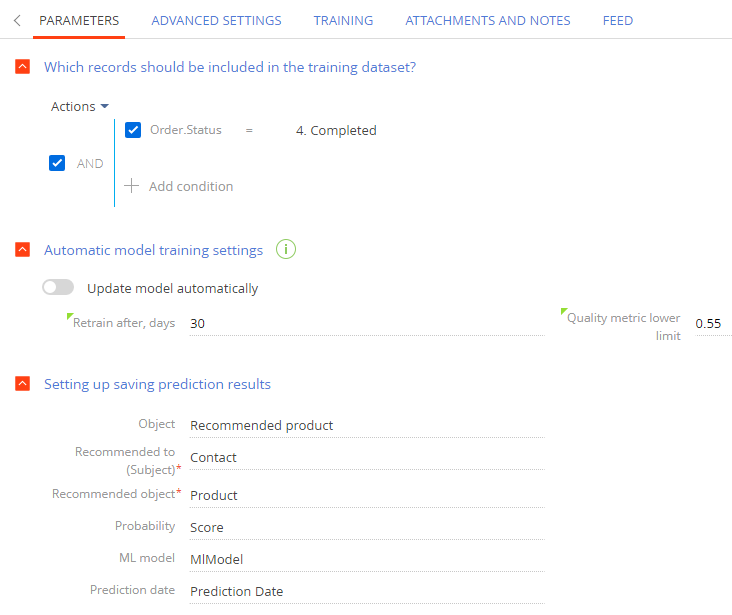
-
3. Add the advanced settings
Click the Advanced settings tab if you need to specify additional prediction model parameters. Fill out the fields similarly to the settings for the lookup value prediction model. Additionally, check the auto-populated values in the fields specific to this ML model.
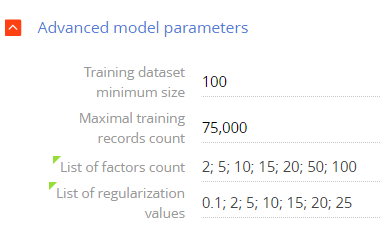
- List of factors count – a pre-configured list of metric numbers for each recommendation object and subject. Creatio will analyze this list to prepare the recommendations.
- List of regularization values – a pre-configured list of additional restrictions. Creatio will add the restrictions to minimize errors and avoid model retraining.
Fig. 5 The advanced model parameters
Prediction result
This will add a new model to Creatio. You will be able to use the model to run processes that predict recommendations for the selected Creatio objects.
Learn more: Configure a prediction business process.
In this example, the product recommendation model will analyze the relationship between the recommendation subject as well as other similar subjects with the Product in order object and generate a recommendation list. The training record selection will be restricted to completed orders. Creatio will rank the recommendation list based on the number of purchased products. Note that recommendation prediction will be performed only for those customers (recommendation subjects) and products (recommendation objects) that were part of the training, i.e., were included in the training selection.
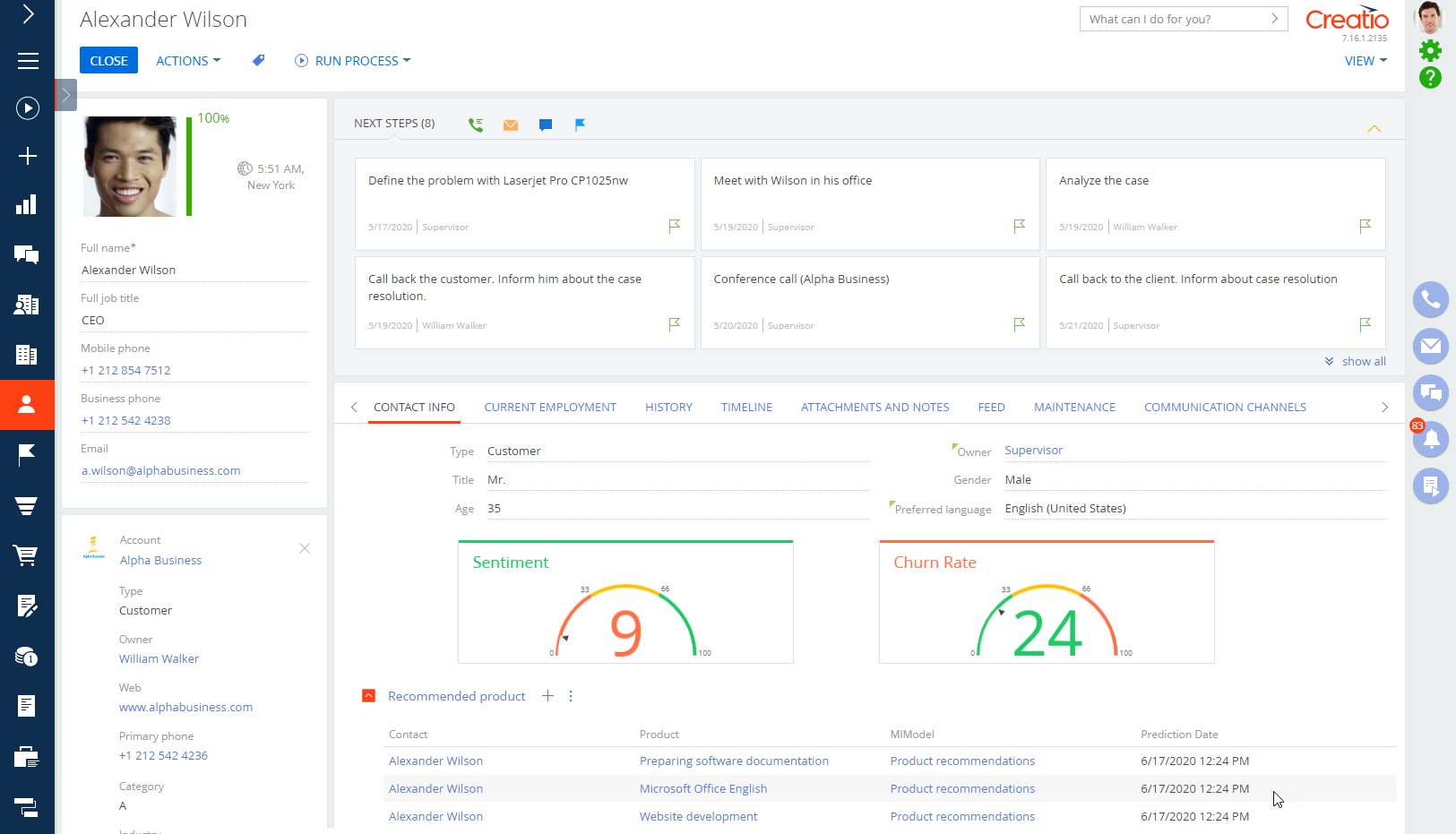
As a result, Creatio will display the recommended products on the relevant contact pages’ Recommended products detail (Fig. 6):