The Exchange Listener synchronization service synchronizes Creatio with MS Exchange and IMAP/SMTP mail services using a subscription mechanism.
This article covers deploying the Exchange Listener synchronization service for Creatio installed on-site.
The service consists of two required components:
-
The Exchange Listener primary module.
-
NoSQL Redis DBMS.
The Exchange Listener module initiates the outgoing connection to EWS API. It uses the mailbox credentials and creates a subscription to “new message” events. The open subscription remains in the component memory to ensure fast response time when new emails arrive. When a corresponding event is received, the email instance loads.
Using an in-memory repository will be enough for deploying the service.
Redis DBMS enables creating a scalable and fault-tolerant system of processing nodes. The Redis repository holds information about the mailboxes that are served. This lets any container process Creatio queries for adding a new subscription or check the status of a specific subscription regardless of the subscription node.
Redis requirements:
-
Anonymous access allowed.
-
Separate database available for the Exchange Listener service operation.
Exchange Listener deployment methods
We recommend using the Kubernetes orchestrator and Helm package manager to deploy the service. Read more >>>
You can also use Docker to speed up the deployment in the development environment. Read more >>>
Deploy the synchronization service via Kubernetes
To deploy the Exchange Listener synchronization service in Docker:
-
Set up the target environment first:
-
The Kubernetes cluster. Read more about how to set up and manage the cluster on the Kubernetes documentation website.
-
The Helm package manager. Read more about installing the package manager on the Helm documentation website.
-
-
Install Redis. Use the GitHub website to learn more about how to install Redis using Helm.
Example of a command for installing Redis:Where:
default – the name of the namespace where Redis will be installed.
redis – an arbitrary name for the Redis instance.
- Install the Exchange Listener module. To install the module, download the helm package. Find the available parameters of the helm package in the table below.
Example of a command for installing Exchange Listener using the service address and relative path:
Where:
<redis_host> – Redis server address.
<Kubernetes_url> – Kubernetes URL or IP address.
Exchange Listener address: <kubernetes_url>/<listener_path>.
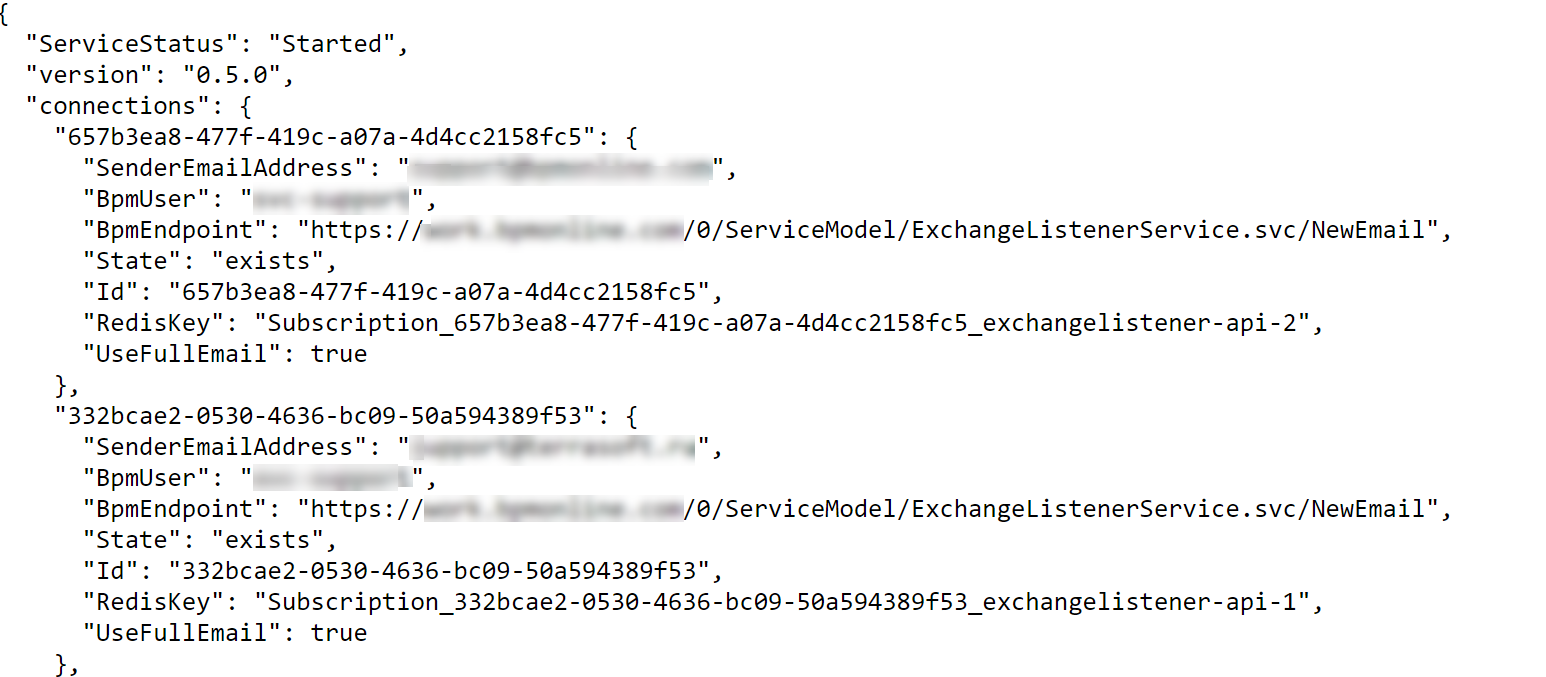
To check whether the Exchange Listener service is available, execute the following request: <kubernetes_url>/<listener_path>/api/listeners/status (Fig. 1).
Example of installing the Exchange Listener using Node IP and port address:
Exchange Listener address – <node_IP:node_port>.
To check whether the address is available, execute the following request: <node_IP:node_port>/api/listeners/status (Fig. 1).
Available parameters of the Exchange Listener helm package
|
Parameter |
Parameter description |
Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
replicaCount |
Number of StatefulSet processors |
2 |
|
service.type |
Service type. You can find more information about the Kubernetes service types in the Kubernetes documentation. |
ClusterIP |
|
service.nodePort |
If the service.type parameter equals NodePort, specify the external service port in this parameter. Read more about the NodePort type in the Kubernetes documentation. |
|
|
env.host |
Host address for Redis. |
|
|
env.port |
Host port for Redis. |
6379 |
|
env.base |
Database number for Redis. |
0 |
|
ingress.enabled |
Use address overriding via ingress. |
false |
|
ApiUrl |
Service address if ingress.enabled=true |
|
|
ingress.path |
Service relative path. |
|
|
log4Net.level |
Logging level by default. |
Info |
Use the requirements calculator to check the server requirements.
Deploy the synchronization service in Docker
To set up the service, use a server (computer or virtual machine) with Linux or Windows OS installed.
To deploy the Exchange Listener synchronization service in Docker:
-
Set up the target environment first:
-
Docker container platform. Read more about how to install and set up the platform on the Docker documentation website.
-
Redis DBMS. To install the Redis Server, use the Windows setup file or the Linux Guide. Make sure you deploy an anonymous Redis DBMS. Learn more about deploying Redis DBMS in Docker on the Docker Hub community website.
-
-
Install and run the Exchange Listener module. To do this, download and deploy the Docker container image.
Below is the example of a command for downloading and running the image via the command line and Docker installed.
Where:
<localhost_port> – local server port.
<redis_host> – Redis server address.
<redis_database_number> – DB number of the Redis server.
<service_name> – service name (entered manually).
<listener_version> – the Listener microservice version.
To check whether the deployed Docker container is available, run the following command:
Exchange Listener service address – localhost:<localhost_port>.
To check whether Exchange Listener service address is available, execute the following request: <Localhost:<localhost_port>/api/listeners/status (Fig. 2).
Set up the Exchange Listener service on Creatio's end
-
Make sure the ExchangeListenerService anonymous service is available at Creatio application address/0/ServiceModel/ExchangeListenerService.svc (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 Example of a response from ExchangeListenerService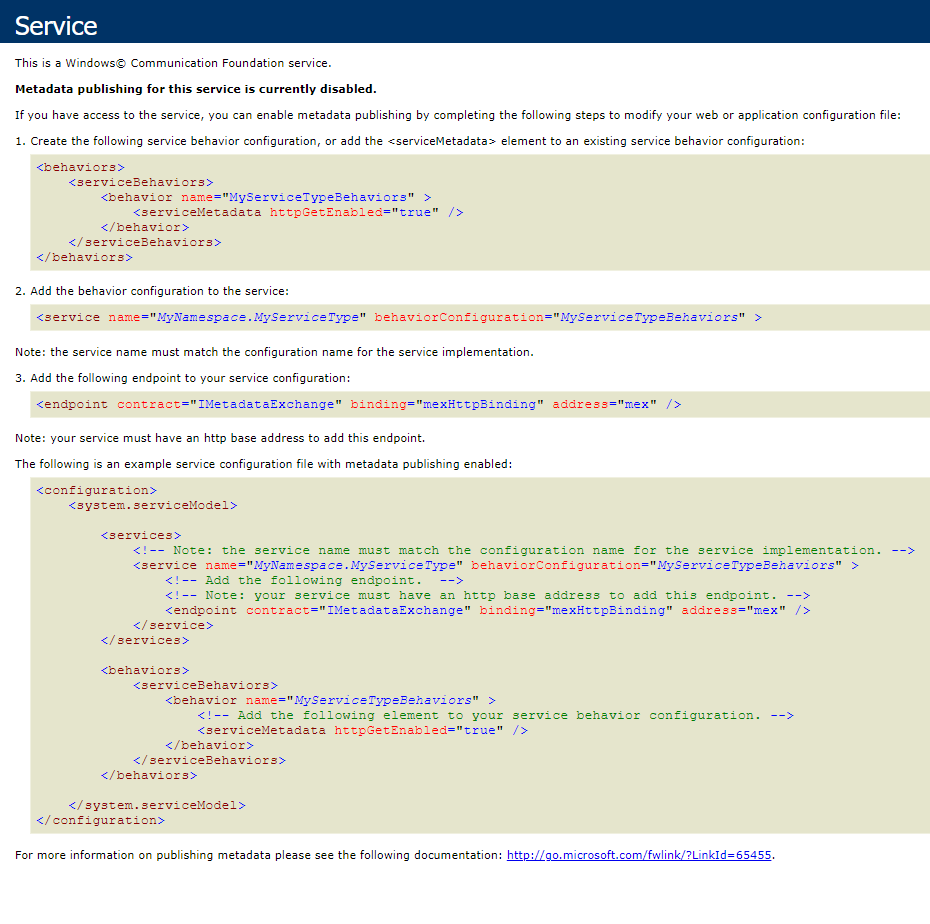
-
Set the needed system setting values. To do this:
-
Open the System Designer, e. g., by clicking
 .
. -
Click “System settings” in the “System setup” block.
-
Set the system setting values as follows:
“ExchangeListenerServiceUri” (“ExchangeListenerServiceUri” code). The format of the system setting value: the service address used at installation/api/listeners.
“Creatio exchange events endpoint URL” (“BpmonlineExchangeEventsEndpointUrl” code). The format of the system setting value: the anonymous ExchangeListenerService address/NewEmail. For example, https://mycreatio.com/0/ServiceModel/ExchangeListenerService.svc/NewEmail.
-
Exchange Listener Service Diagnostics
The Exchange Listener service diagnostics page provides tools for troubleshooting the Exchange Listener service.
Use the service page to:
-
Check if the features essential for Exchange Listener are enabled.
-
Verify the service availability.
-
Receive subscription information.
-
Validate the “ExchangeListenerServiceUri” system setting.
-
Check the health of a mailbox.
To access the Exchange Listener Service Diagnostics page, add the “/0/ClientApp/#/IntegrationDiagnostics/” string to the URL of your Creatio website in the browser address bar and select Enter. For example:
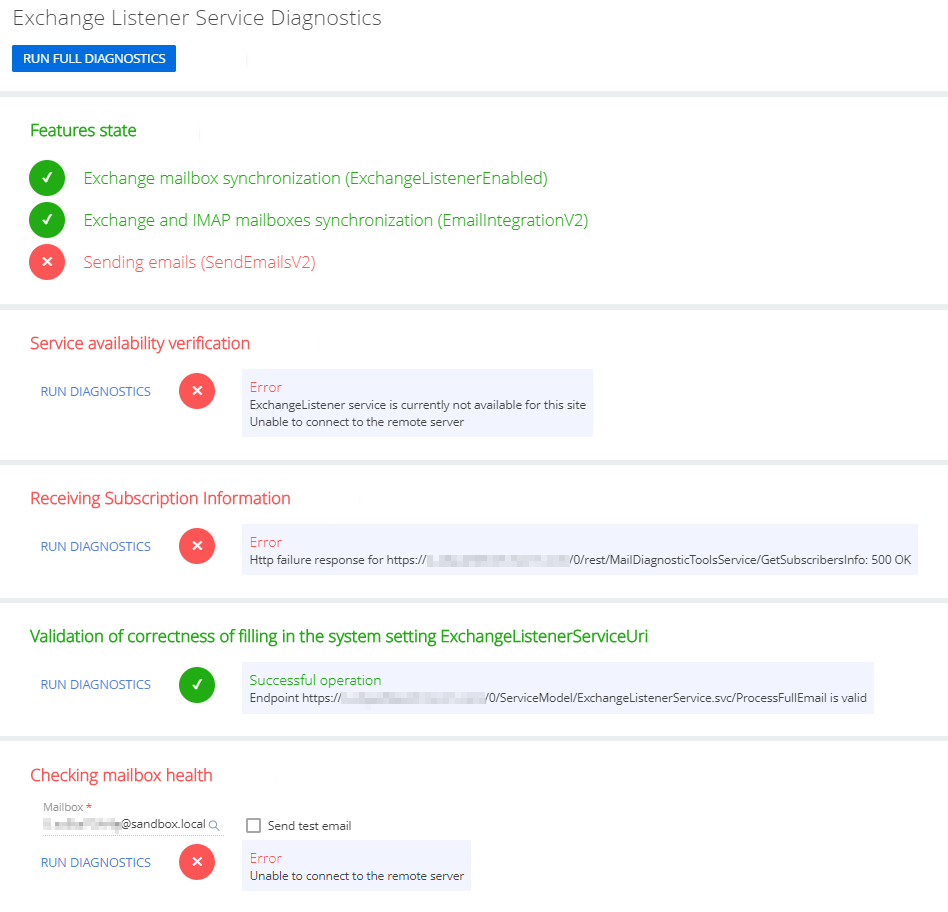
The diagnostics page contains several readout blocks and diagnostics controls (Fig. 3). By default, most of the readout blocks do not display diagnostics data unless you click Run diagnostics in that block.
|
Feature state |
This readout block runs diagnostics automatically on page load. Checks if required Exchange Listener features are enabled in your Creatio application:
Learn more about how to enable Creatio features: Feature Toggle. Mechanism of enabling and disabling functions. |
|
Service availability verification |
Checks if the Exchange Listener service is accessible from your Creatio application. |
|
Receiving subscription information |
Checks the connection to the remote server. |
|
Validation of the “ExchangeListenerServiceUri” system setting |
Checks if the Exchange Listener service endpoint specified in the “ExchangeListenerServiceUri” system setting is valid. |
|
Checking mailbox health |
Checks the operation of MS Exchange mailboxes. Select the Send test email checkbox to send a test email to the specified address when clicking the Run diagnostics link. |