How do I check which version of the global search service I have?
If you use Creatio cloud, you will always have the latest version of the global search service.
If you use Creatio on-site, run the following console command:
This will open the list of all running containers. The number of global search version will be available in the image column.
How do I initiate the re-indexing of my Creatio site?
For global search version 2.0 and later:
Execute the PUT request in this format:
For global search versions earlier than 2.0:
-
Open gs-mysql container via the following command:
-
Run the following command in the opened gs-mysql container:
How do I enable the global search service logging?
By default, the service logs only errors. To enable logging of all events, locate the following string in the docker-compose.yaml file:
Replace the string with the following string:
Which metrics and tracking schema can I use to monitor the global search operation?
Execute the following request:
Here, GS-WEB-API is the server address, and SITE_NAME is your Creatio website name.
How do I set up access to ElasticSearch via a password?
You can restrict access to ElasticSearch using Haproxy that supports base64 authentification. Use the x-pack plugin to set up access to ElasticSearch via a login and a password.
How do I add a new object to the ElasticSearch indexing, or change the settings for the indexed fields of existing objects?
In Creatio version 7.18.4 and earlier, you can enable and configure indexing of specific sections using Creatio in-app tools. By default, ElasticSearch will index only sections regardless of their author, as well as string and lookup columns (with a few exceptions). View the up-to-date list of exceptions in the attached *.pdf file.
Since Creatio version 7.18.5, you can optimize columns indexed for global search. To improve Creatio performance and reduce the load on the server, you can specify the columns to exclude from global search indexing explicitly. For example, columns that contain service information.
To modify the list of indexed columns:
-
Open the System Designer. For example, click the
 button.
button. -
Click System settings in the System setup block (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 The System settings section
-
Select the “GlobalSearchIndexedDataConfig” (“GlobalSearchIndexedDataConfig” code) system setting in the list and click the Open button.
- The Default value field on the system setting page contains the JSON list of columns to exclude from indexing (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 The field that contains the list of columns to exclude from indexing
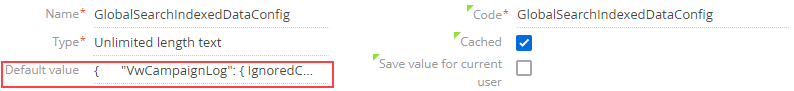
-
Copy the list of columns to exclude from indexing and edit it externally. You can do it in any online JSON editor.
The list of columns to exclude from indexing consists of blocks. Each block contains a unique object code, which you can find in the Code field in the Configuration section. View an example of the block structure below:
- Validate the JSON string you edited, for example, in an online editor.
- Paste the updated list to the Default value field and save the changes.
- Restart the indexing to force update the column list in ElasticSearch.
How do I deploy ElasticSearch on several servers with a single URL? How do I set up clustering?
Learn more in the Elastic service documentation.
Why is the “Duplicates search rules” setting not displayed for me?
Check if the “Deduplication service api address” (“DeduplicationWebApiUrl” code) system setting is populated and whether the following features are enabled in “FeatureToggle:”
- “BulkESDeduplication”
- “ESDeduplication”
- “Deduplication”
Learn more about enabling additional functionality in developer documentation: Feature Toggle mechanism.
Can I use the global search and bulk duplicate search services in two Creatio applications simultaneously?
If you are using two Creatio applications, for example, production and developer environments, you can set up the global search and bulk duplicate search services for each of them independently. Use the following guides to set up the services:
How does Creatio sort the search results?
The display order of the search results mainly depends on their relevance. The following factors affect relevance:
- The volume of text in the document.
- The frequency of the search query in the document.
- The frequency of the search query in the index, as well as other, less important, parameters.
The following system settings affect the display order of search results as well:
- “Global search default entity weight” (“GlobalSearchDefaultEntityWeight” code). Increases the display priority of section records where the search was performed. For example, if you enter a search query from the Contacts section, the records of this section will appear first in the list.
- “Global search default primary column weight” (“GlobalSearchDefaultPrimaryColumnWeight” code). Increases the display priority of specific search results. It applies to records whose primary column value matches the search query. For example, Full name is a primary column for the contact, and Name is a primary column for the account. If the search query matches the value in the record’s primary column, this record will be displayed at the top of the search results.
While these system settings affect relevance, they do not guarantee the exact display order of search results as the other factors affect the order as well.
Do microservices support Windows authentication?
Since you must deploy the global search and deduplication service using Docker, microservices do not support Windows authentication.
How do I configure phone number indexing per character?
Global Search automatically indexes phone numbers per character and can find them using partial matches. If you have added custom communication options of the Phone type, the default indexing mode is the exact match, and you can configure indexing per character by using the "Global Search Telephone Number Columns" system setting (code: GlobalSearchTelephoneNumberColumns).
The "Global Search Telephone Number Columns" system setting is available for Creatio version 8.0.7 and later. To customize this feature, use a JSON string in the Default value field to list objects as JSON keys and field names of the Phone type as their array values to index them individually per character, then save the setting.
For example, configure Global Search Telephone Number Columns as follows: