Data-operations (front-end)
The functionality is relevant to Classic UI.
Front-end Creatio modules implement data management using the high-level EntitySchemaQuery class that builds database selection queries.
The major features of the EntitySchemaQuery class:
- Data selection queries created using
EntitySchemaQueryapply the access permissions of the current user. - The caching mechanism lets you optimize operations by accessing cached query results without direct access to the database.
The data management procedure for front-end Creatio modules is as follows:
- Create an instance of the
EntitySchemaQueryclass. - Specify the root schema.
- Configure a path to the root schema column to add the column to the query.
- Create filter instances.
- Add the filters to the query.
- Filter the query results.
Configure the column paths relative to the root schema
Base an EntitySchemaQuery query on the root schema. The root schema is the database table relative to which to build paths to the query columns, including the columns of the joined tables. To use a table column in a query, set the path to the column correctly.
Specify the column path using direct connections
The template for configuring the column path using the direct connections of LookupColumnName.LookupSchema’sColumnSchemaName.
For example, a [City] root schema contains a [Country] lookup column. The column is connected to the [Country] lookup schema via the Id column.
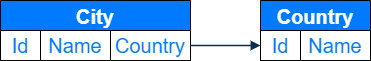
The path to the column that contains the name of the country connected to the city, built using the direct connections Country.Name. Where:
Countryis the name of the lookup column in the[City]root schema. Links to the[Country]schema.Nameis the name of the column in the[Country]lookup schema.
Specify the column path using the reverse connections
The template for configuring the column path using the reverse connections [JoinableSchemaName:NameOfTheColumnToLinkTheJoinableSchema:NameOfTheColumnToLinkTheCurrentSchema].JoinableSchema’sColumnName.
The path to the column that contains the name of the contact who added the city, built using the reverse connections [Contact:Id:CreatedBy].Name. Where:
Contactis the name of the joinable schema.Idis the name of the[Contact]schema’s column to connect the joinable schema.CreatedByis the name of the[City]schema's lookup column to connect the current schema.Nameis the value of the[City]schema's lookup column.
If the schema’s lookup column to connect the current schema is [Id], you do not have to specify it: [JoinableSchemaName:NameOfTheColumnToConnectTheJoinableSchema].RootSchema’sColumnName. For example, [Contact:City].Name.
Add the columns to the query
The EntitySchemaQuery query column is a Terrasoft.EntityQueryColumn class instance. Specify the main features in the column instance properties:
- header
- value for display
- usage flags
- sorting order and position
Add columns to the query using the addColumn() method that returns the query column instance. The addColumn() methods configure the name of the column relative to the root schema according to the rules described above: Configure the column paths relative to the root schema. The variations of the addColumn() method let you add query columns that contain different parameters. View the variations in the table below.
Column type | Method |
|---|---|
The column by the specified path relative to the root schema | addColumn(column, columnAlias) |
The instance of the query column class | |
The parameter column | addParameterColumn(paramValue, paramDataType, columnAlias) |
The function column | addFunctionColumn(columnPath, functionType, columnAlias) |
The aggregative function column | addAggregationSchemaColumnFunctionColumn(columnPath, aggregationType, columnAlias) |
Retrieve the query results
The result of the EntitySchemaQuery query is a collection of Creatio objects. Each collection instance is a dataset string returned by the query.
The ways to retrieve the query results are as follows:
- Call the
getEntity()method to retrieve a particular dataset string by the specified primary key. - Call the
getEntityCollection()method to retrieve the entire resulting dataset.
Manage the query filters
Filters are sets of conditions applied when displaying the query data. In SQL terms, a filter is a separate predicate (condition) of the WHERE operator.
To create a simple filter in EntitySchemaQuery, use the createFilter() method that returns the created object of the Terrasoft.CompareFilter filter. EntitySchemaQuery implements methods that create special kinds of filters.
The EntitySchemaQuery instance contains the filters property that represents the filter collection of the query (the Terrasoft.FilterGroup class instance). The Terrasoft.FilterGroup class instance is a collection of Terrasoft.BaseFilter elements.
Follow this procedure to add a filter to the query:
- Create a filter instance for the query (the
createFilter()method, methods that create special kinds of filters). - Add the filter instance to the query filter collection (the
add()collection method).
By default, Creatio uses the logical AND operation to combine the filters added to the filters collection. The logicalOperation property of the filters collection lets you specify the logical operation for combining filters. The logicalOperation accepts the values of the Terrasoft.core.enums.LogicalOperatorType enumeration (AND, OR).
EntitySchemaQuery queries let you manage the filters involved in the creation of the resulting dataset. Each element of the filters collection includes the isEnabled property that determines whether the element takes part in building the resulting query (true/false). Creatio defines the similar isEnabled property for the filters collection. If you set this property to false, the query filtering will be disabled, yet the query filters collection will remain unchanged. Thus, you can create a query filters collection and use various combinations without modifying the collection directly.
Configure the column paths in the EntitySchemaQuery filters according to the general rules for configuring the paths to columns relative to the root schema.