Script task process element
The Script-task process element is a system action that executes the C# code and facilitates its interaction with other elements of the business-process. Use this element to implement logic that the standard process elements cannot provide, for example:
- complex computations
- processing records in bulk
- looping
- other tasks that are hard to implement using the stadard designer elements
- as a replacement to a sequence of several and more Formula elements.
Follow the guidelines below to work with the Script task element.
- Maintain the code structure. Test the element after saving by running the business process. The correctness of the code and the element’s performance depend on the code quality and the developer’s qualification.
- Comment the main blocks of code and tasks performed by the Script task element to explain the function, purpose, and effects of each code part. This helps users better understand what the process does, and facilitates grasping the process workflow by developers.
- Specify the exact names of third-party schemas when using them. Follow these guidelines when coding third-party schemas.
- Avoid temporary fixes, since non-standardized code impairs the ability to maintain it. When process errors are encountered, make sure they are fixed correctly.
- End the code in Script task element with
return true;line.
To edit the script code, double-click the element on the diagram. The element setup area will open, where you can enter and edit the script code (Fig. 1).
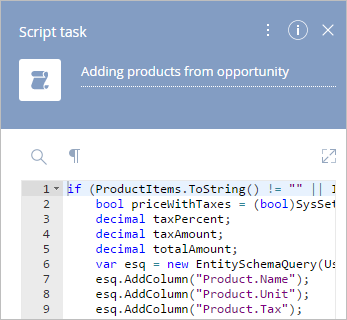
 – expand the script code window.
– expand the script code window.
 – collapse the script code window.
– collapse the script code window.
 – search text in the script code.
– search text in the script code.
 – show the hidden symbols in the text code (for example, spaces, tabulations).
– show the hidden symbols in the text code (for example, spaces, tabulations).
Creatio enables you to execute processes without publishing them. However, the use of methods and Script-task elements requires the schema publication. For more information about calling business process methods, please refer to the "Web service methods" article
Get and Set methods
All new business processes in Creatio are interpreted. Use the Get and Set methods (Fig. 2) to reference the parameter values of an interpreted process.
The Get method returns the value of an item or process.
Method signature:
Get<T>(string path)
T — parameter value type.
path — a string that specifies the path to a parameter or property. The path is built according to these rules:
- "parameter name"
- "property name"
- "element name.parameter name"
- "element name.property name"
The Set method sets the value of an item or process.
Method signature:
Set<T>(String path, value)
value — the specified value.
path — a string that specifies the path to a parameter or property. The path is built according to the rules described above for the Get method:
"T" – a generic type parameter not specific to a particular data type that accepts the passed type value. Conversion between Creatio and C# parameters is shown in the table below.
Conversion between Creatio and C# parameters
Creatio parameter type | C# parameter type |
|---|---|
Integer | int |
Decimal (0.00000001) | decimal |
Decimal (0.0001) | |
Decimal (0.001) | |
Decimal (0.01) | |
Decimal (0.1) | |
Currency | |
Date/time | DateTime |
Date | |
Time | |
Unique identifier | Guid |
Lookup | |
Boolean | bool |
Text (50 characters) | string |
Text (250 characters) | |
Text (500 characters) | |
Unlimited length text | |
Non-localizable string | |
Collection of values | IObjectList and any classes that implement these interfaces |
Collection of records | ICompositeObjectList<ICompositeObject> and any classes that implement these interfaces |
Examples of working with type parameters
int integerValue = Get<int>("IntegerParameter");
integerValue += 5;
Set<int>("IntegerParameter", integerValue);
decimal decimalValue = Get<decimal>("DecimalParameter");
decimalValue += 5.5m;
Set<decimal>("DecimalParameter", decimalValue);
Guid uniqueIdentifierValue = Get<Guid>("UniqueIdentifierParameter");
if (uniqueIdentifierValue != Guid.Empty) {
uniqueIdentifierValue = Guid.Empty;
Set<Guid>("UniqueIdentifierParameter", uniqueIdentifierValue);
}
DateTime dateTimeValue = Get<DateTime>("DateTimeParameter");
dateTimeValue = dateTimeValue.AddDays(1);
Set<DateTime>("DateTimeParameter", dateTimeValue);
Guid lookupValue = Get<Guid>("LookupParameter");
if (lookupValue.IsEmpty()) {
lookupValue = (Guid)UserConnection.SystemValueManager.GetValue(UserConnection, "CurrentUserContact");
Set<Guid>("LookupParameter", lookupValue);
}
string textValue = Get<string>("TextParameter");
textValue += " and something else";
Set<string>("TextParameter", textValue);
LocalizableString localizableStringValue = Get<LocalizableString>("LocalizableStringParameter");
CultureInfo cultureFr = CultureInfo.GetCultureInfo("fr-FR");
CultureInfo cultureEn = CultureInfo.GetCultureInfo("en-US");
localizableStringValue.SetCultureValue(cultureFr, "Bonjour!");
localizableStringValue.SetCultureValue(cultureEn, "Hello!");
Set<LocalizableString>("LocalizableStringParameter", localizableStringValue);
bool booleanValue = Get<bool>("BooleanParameter");
booleanValue = !booleanValue;
Set<bool>("BooleanParameter", booleanValue);
ObjectList<int> numbers = ObjectList.Create(1, 2, 3, 4);
Set<ObjectList<int>>("IntegerValuesParameter", numbers);
var items = Get<ObjectList<int>>("IntegerValuesParameter");
items.Add(5);
Set<ObjectList<int>>("IntegerValuesParameter", items);
ObjectList<bool> booleanValues = ObjectList.Create(false, true, true, false);
Set<ObjectList<bool>>("BooleanValuesParameter", booleanValues);
booleanValues = Get<ObjectList<bool>>("BooleanValuesParameter");
if (booleanValues.Count == 4) {
booleanValues.Clear();
}
Set<ObjectList<bool>>("BooleanValuesParameter", booleanValues);
ObjectList<DateTime> dateTimeValues = ObjectList.Create(new DateTime(2020, 08, 03, 13, 15, 14), DateTime.Now);
Set<ObjectList<DateTime>>("DateTimeValuesParameter", dateTimeValues);
ObjectList<Guid> guidValues = ObjectList.Create(Guid.NewGuid(), Guid.NewGuid());
Set<ObjectList<Guid>>("GuidValuesParameter", guidValues);
guidValues = Get<ObjectList<Guid>>("GuidValuesParameter");
if (!guidValues.Contains(Guid.Empty)) {
guidValues.Add(Guid.Empty);
}
Set<ObjectList<Guid>>("GuidValuesParameter", guidValues);
ObjectList<decimal> decimalValues = ObjectList.Create(3.14m, 432434.00032m);
Set<ObjectList<decimal>>("DecimalValuesParameter", decimalValues);
decimalValues = Get<ObjectList<decimal>>("DecimalValuesParameter");
decimalValues.RemoveAt(1);
Set<ObjectList<decimal>>("DecimalValuesParameter", decimalValues);
ObjectList<string> stringValues = ObjectList.Create("string value 1", "string value 2");
Set<ObjectList<string>>("StringValuesParameter", stringValues);
stringValues = Get<ObjectList<string>>("StringValuesParameter");
stringValues.Remove("string value 1");
Set<ObjectList<string>>("StringValuesParameter", stringValues);
var list = Get<ICompositeObjectList<ICompositeObject>>("ReadDataUserTask1.ResultCompositeObjectList");
var sb = new StringBuilder();
foreach (ICompositeObject item in list) {
if (item.TryGetValue<string>("Name", out string value)) {
sb.Append(value).Append(" | ");
}
}
Set<string>("FieldsOfCompositeObjectListParameter", sb.ToString());
var list = new CompositeObjectList<CompositeObject>();
var item1 = new CompositeObject();
item1["Id"] = Guid.NewGuid();
item1["Name"] = "Name1";
list.Add(item1);
var item2 = new CompositeObject();
item2["Id"] = Guid.NewGuid();
item2["Name"] = "Name2";
list.Add(item2);
Set<CompositeObjectList<CompositeObject>>("CompositeObjectListParameter", list);