Connect a custom web service to machine learning service
Connect a custom web service to machine learning (ML) functionality. The service implements custom predictive scoring and is developed using Microsoft Visual Studio Code.
1. Implement custom predictive scoring
Download and unpack the *.zip archive that includes the web service. The service implements custom predictive scoring in a Microsoft Visual Studio Code project.
To develop a custom web service using a Microsoft Visual Studio Code project, follow the instructions in a separate article: Develop C# code in a configuration project.
The MLService web service implements the following endpoints:
session/startdata/uploadsession/info/getfakeScorer/beginTrainingfakeScorer/predict
2. Expand the problem list of the ML service
-
Click
 to open the System Designer.
to open the System Designer. -
Go to the System setup block → Lookups.
-
Open the ML problem types lookup.
-
Add a problem type.
-
Click New on the lookup toolbar.
-
Fill out the problem type properties.
- Set Name to "Fake scoring."
- Set Service endpoint Url to "http://localhost:5000/."
- Set Training endpoint to "/fakeScorer/beginTraining."
-
-
Find an ID of the problem type. To do this, display the corresponding column in the lookup list.
- Click View → Select fields to display on the lookup toolbar.
- Add the column to the lookup list. To do this, click
 and select the Id column.
and select the Id column. - Click Select → Save.
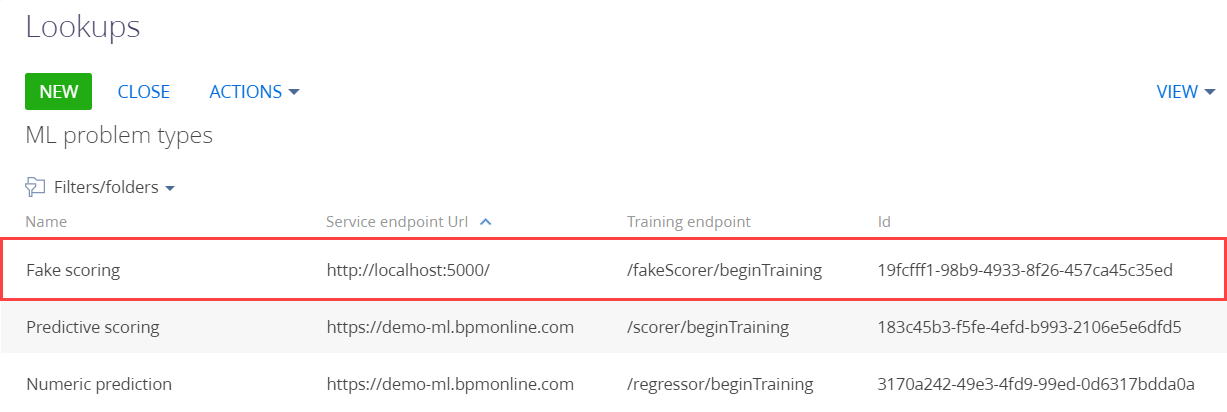
The ID of the Fake scoring problem type is 19fcfff1-98b9-4933-8f26-457ca45c35ed.
3. Implement a ML model
-
Go to the Configuration section and select a user-made package to add the schema.
-
Click Add → Page view model on the section list toolbar.
-
Fill out the schema properties.
- Set Code to "UsrMLModelPage."
- Set Title to "MLModelPage."
- Select "MLModelPage" in the Parent object property.

-
Implement the style of the new mini page similar to the mini page for creating a predictive scoring model. To do this, overload the
getIsScoring()method.View the source code of the view model schema of the page below.
UsrMLModelPagedefine("UsrMLModelPage", [], function() {
return {
/* The name of the page object schema. */
entitySchemaName: "MLModel",
/* The properties of the page view model. */
properties: {
FakeScoringProblemTypeId: "19fcfff1-98b9-4933-8f26-457ca45c35ed"
},
/* The methods of the page view model. */
methods: {
getIsScoring: function() {
const parentResult = this.callParent(arguments);
return parentResult || this.getLookupValue("MLProblemType") === this.FakeScoringProblemTypeId;
}
}
};
}); -
Click Save on the Module Designer's toolbar.
4. Implement the handling of the ML model results
-
Go to the Configuration section and select a user-made package to add the schema.
-
Click Add → Source code on the section list toolbar.
-
Fill out the schema properties.
- Set Code to "UsrFakeScoringEntityPredictor."
- Set Title to "FakeScoringEntityPredictor."
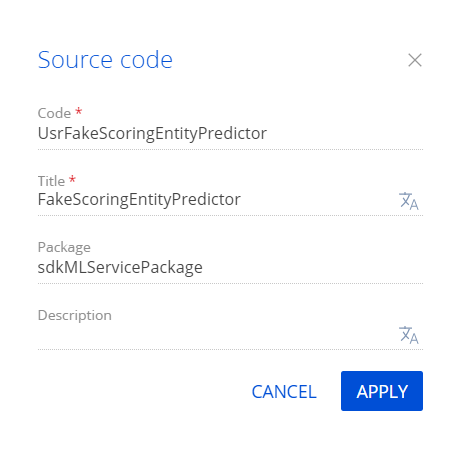
Click Apply to apply the properties.
-
Implement the handling of the ML model results.
- Implement the
Predict()method that receives data exported from Creatio by object and returns the prediction value. The method uses a proxy class that implements theIMLServiceProxyinterface to facilitate web service calls. - Initialize the
ProblemTypeIdproperty using the ID of the Fake scoring problem type from the ML problem types lookup. - Implement the
SaveEntityPredictedValues()andSavePrediction()methods.
View the source code of the
UsrFakeScoringEntityPredictorclass below.UsrFakeScoringEntityPredictornamespace Terrasoft.Configuration.ML
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Core;
using Core.Factories;
using Terrasoft.Core.Process.Configuration;
using Terrasoft.ML.Interfaces;
[DefaultBinding(typeof(IMLEntityPredictor), Name = "19fcfff1-98b9-4933-8f26-457ca45c35ed")]
[DefaultBinding(typeof(IMLPredictor<ScoringOutput>), Name = "19fcfff1-98b9-4933-8f26-457ca45c35ed")]
public class FakeScoringEntityPredictor: MLBaseEntityPredictor<ScoringOutput>, IMLEntityPredictor, IMLPredictor<ScoringOutput>{
public FakeScoringEntityPredictor(UserConnection userConnection) : base(userConnection) {
}
protected override Guid ProblemTypeId => new Guid("19fcfff1-98b9-4933-8f26-457ca45c35ed");
protected override ScoringOutput Predict(IMLServiceProxy proxy, MLModelConfig model, Dictionary<string, object> data, MLDataPredictionUserTask predictionUserTask) {
return proxy.FakeScore(model, data, true);
}
protected override List<ScoringOutput> Predict(MLModelConfig model, IList<Dictionary<string, object>> dataList, IMLServiceProxy proxy, MLDataPredictionUserTask predictionUserTask) {
return proxy.FakeScore(model, dataList, true);
}
protected override void SaveEntityPredictedValues(MLModelConfig model, Guid entityId, ScoringOutput predictedResult) {
var predictedValues = new Dictionary<MLModelConfig, double> {
{
model, predictedResult.Score
}
};
PredictionSaver.SaveEntityScoredValues(model.EntitySchemaId, entityId, predictedValues);
}
protected override void SavePrediction(MLModelConfig model, Guid entityId, ScoringOutput predictedResult) {
PredictionSaver.SavePrediction(model.Id, model.ModelInstanceUId, entityId, predictedResult.Score);
}
}
} - Implement the
-
Click Publish on the Source Code Designer’s toolbar to apply the changes on the database level.
5. Add a new problem type to the prediction method
-
Go to the Configuration section and select a user-made package to add the schema.
-
Click Add → Source code on the section list toolbar.
-
Fill out the schema properties.
- Set Code to "UsrFakeScoringProxy."
- Set Title to "FakeScoringProxy."
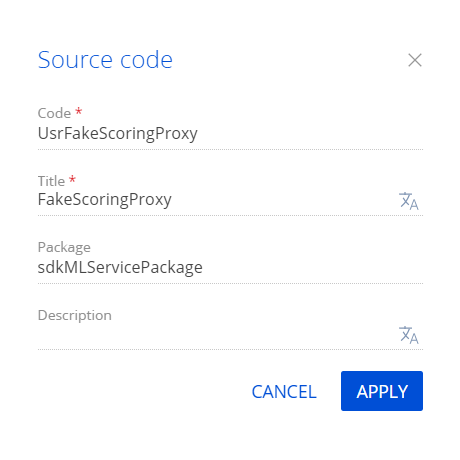
Click Apply to apply the properties.
-
Add the Fake scoring problem type to the prediction method. To do this, extend the
IMLServiceProxybase interface and implementations in the prediction method of the current problem type. TheMLServiceProxyclass implements thePredict()method that receives contracts for input data and prediction results.View the source code of the
UsrFakeScoringProxyclass below.UsrFakeScoringProxynamespace Terrasoft.Configuration.ML
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using Terrasoft.ML.Interfaces;
using Terrasoft.ML.Interfaces.Requests;
using Terrasoft.ML.Interfaces.Responses;
public partial interface IMLServiceProxy
{
ScoringOutput FakeScore(MLModelConfig model, Dictionary<string, object> data, bool predictContributions);
List<ScoringOutput> FakeScore(MLModelConfig model, IList<Dictionary<string, object>> dataList, bool predictContributions);
}
public partial class MLServiceProxy : IMLServiceProxy
{
public ScoringOutput FakeScore(MLModelConfig model, Dictionary<string, object> data, bool predictContributions) {
ScoringResponse response = Predict<ExplainedScoringRequest, ScoringResponse>(model.ModelInstanceUId, new List<Dictionary<string, object>> { data }, model.PredictionEndpoint, 100, predictContributions);
return response.Outputs.FirstOrDefault();
}
public List<ScoringOutput> FakeScore(MLModelConfig model, IList<Dictionary<string, object>> dataList, bool predictContributions) {
int count = Math.Min(1, dataList.Count);
int timeout = Math.Max(ScoreTimeoutSec * count, BatchScoreTimeoutSec);
ScoringResponse response = Predict<ScoringRequest, ScoringResponse>(model.ModelInstanceUId, dataList, model.PredictionEndpoint, timeout, predictContributions);
return response.Outputs;
}
}
} -
Click Publish on the Source Code Designer’s toolbar to apply the changes on the database level.
6. Implement the batch prediction functionality
-
Go to the Configuration section and select a user-made package to add the schema.
-
Click Add → Source code on the section list toolbar.
-
Fill out the schema properties.
- Set Code to "UsrFakeBatchScorer."
- Set Title to "FakeBatchScorer."
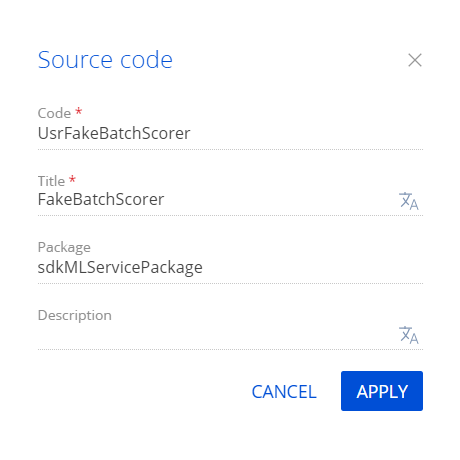
Click Apply to apply the properties.
-
Implement the batch prediction functionality.
- Implement the
IMLBatchPredictorinterface. - Implement the
FormatValueForSaving()andSavePredictionResult()methods.
View the source code of the
UsrFakeBatchScorerclass below.UsrFakeBatchScorernamespace Terrasoft.Configuration.ML
{
using System;
using Core;
using Terrasoft.Core.Factories;
using Terrasoft.ML.Interfaces;
[DefaultBinding(typeof(IMLBatchPredictor), Name = "19fcfff1-98b9-4933-8f26-457ca45c35ed")]
public class FakeBatchScorer : MLBatchPredictor<ScoringOutput>
{
public FakeBatchScorer(UserConnection userConnection) : base(userConnection) {
}
protected override object FormatValueForSaving(ScoringOutput scoringOutput) {
return Convert.ToInt32(scoringOutput.Score * 100);
}
protected override void SavePredictionResult(MLModelConfig modelConfigDiff, Guid entityId, ScoringOutput value) {
PredictionSaver.SavePrediction(modelConfigDiff.Id, modelConfigDiff.ModelInstanceUId, entityId, value);
}
}
} - Implement the
-
Click Publish on the Source Code Designer’s toolbar to apply the changes on the database level.
Resources
Package with example implementation
Configuration project with web service functionality implementation (for .NET 6)
Configuration project with web service functionality implementation (for .NET Core 3.1)